Inquire
REMOTE PATIENT MONITORING WEARABLE SYSTEM
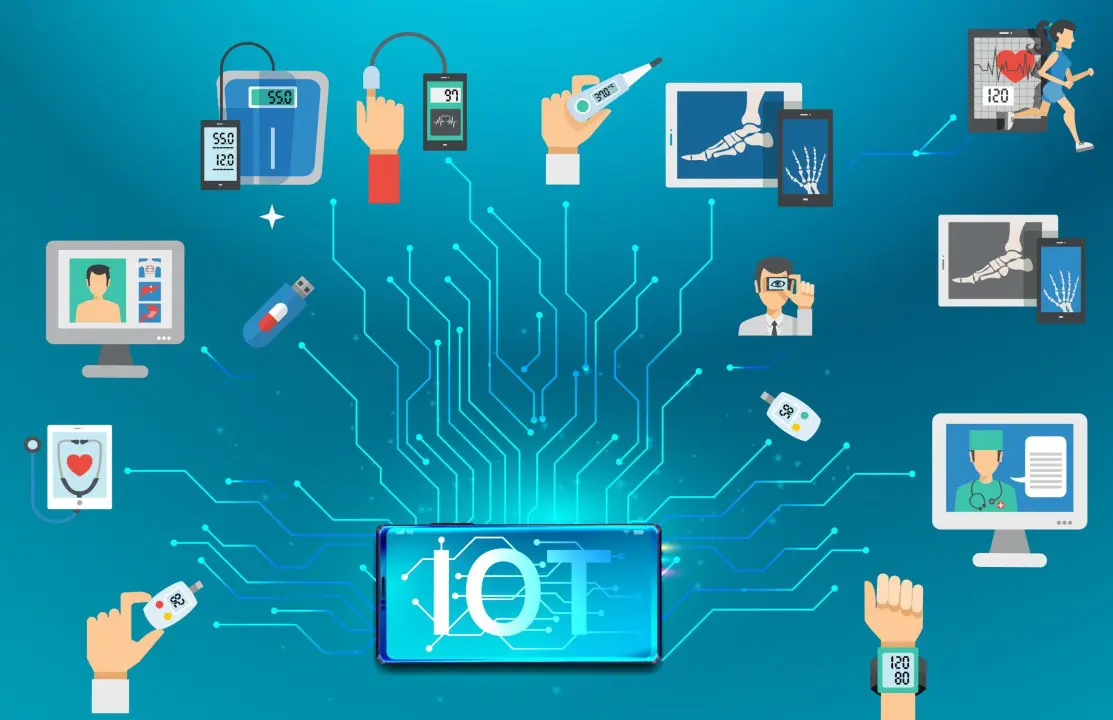
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) wearable devices represent a breakthrough in healthcare technology, enabling continuous, non-invasive monitoring of patients’ physiological parameters outside traditional clinical environments. These smart wearables are embedded with an array of biosensors and wireless communication modules that allow the collection, processing, and real-time transmission of vital health data. The core objective of RPM systems is to support proactive healthcare by facilitating early detection of potential health issues, especially in patients with chronic illnesses, elderly populations, and post-operative individuals. Typically, these wearable devices are equipped with sensors that monitor key health indicators such as heart rate, electrocardiogram (ECG), blood pressure, body temperature, blood oxygen saturation (SpO2), respiratory rate, blood glucose level, and physical activity through accelerometers and gyroscopes. The data from these sensors is processed using a microcontroller unit (MCU), which performs signal conditioning, initial data filtering, and data packaging for transmission.
Communication technologies such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Wi-Fi, LTE, and NB-IoT are integrated into these wearables to enable secure and energy-efficient data transfer to mobile applications or cloud-based servers. These cloud platforms are designed to store large volumes of data and support advanced analytics using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. These algorithms help in pattern recognition, anomaly detection, and predictive diagnostics, thereby providing timely alerts and recommendations to both patients and healthcare providers. Moreover, the wearables are generally powered by compact lithium-ion batteries with power management systems that ensure long battery life to support continuous operation. The integration with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems further enhances data accessibility for clinicians and allows seamless updates to patient records.
The applications of RPM wearables are vast and impactful. They are extensively used in chronic disease management for conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders. In elderly care, these devices enable fall detection, medication adherence tracking, and emergency alert systems, which are vital for aging-in-place models. Post-surgical patients benefit from remote monitoring of recovery indicators, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enabling early identification of complications. During pandemics, such as COVID-19, RPM wearables have played a crucial role in remotely monitoring patients in quarantine, thereby reducing the risk of virus transmission and ensuring timely medical intervention.
Despite the technological advantages, RPM wearables face several challenges. Ensuring data security and privacy is critical, especially with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR governing health data. Accuracy and reliability of sensor measurements under varying conditions, user adherence to regular usage, interoperability with diverse healthcare IT systems, and device affordability are also important concerns that need to be addressed for large-scale adoption. However, ongoing advancements in sensor technologies, edge computing, battery efficiency, and AI analytics continue to enhance the reliability, comfort, and intelligence of these systems. In conclusion, Remote Patient Monitoring wearables are revolutionizing the healthcare industry by enabling real-time, data-driven, and patient-centric care. As this technology matures, it holds the promise to significantly reduce healthcare costs, enhance early diagnosis, and improve overall patient outcomes in the evolving landscape of digital and connected health.
- Managerial Effectiveness!
- Future and Predictions
- Motivatinal / Inspiring
- Autre
- Entrepreneurship
- Mentoring & Guidance
- Marketing
- Networking
- HR & Recruiting
- Literature
- Shopping
- Career Management & Advancement

 SkillClick
SkillClick