Inquire
UI and UX
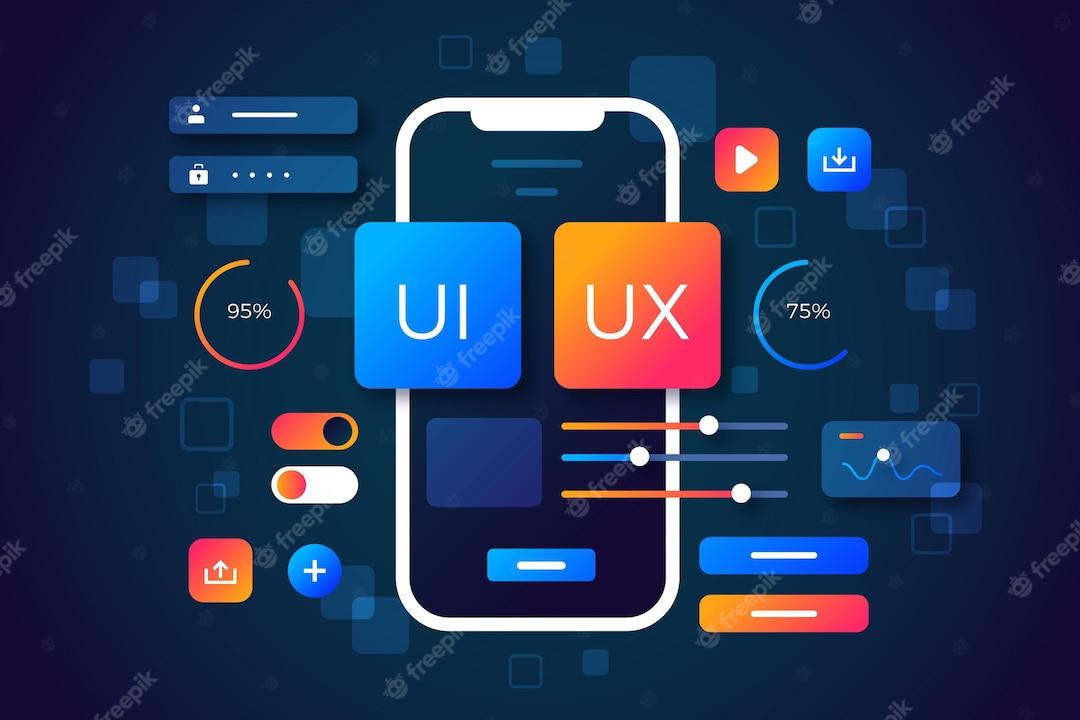

User Interface (UI):
UI, or User Interface, refers to the visual and interactive elements that users interact with when using a digital product, such as a website, app, or software. It includes everything that users see and interact with on the screen, from buttons and icons to text fields and images. The goal of UI design is to create an aesthetically pleasing and intuitive interface that guides users through their interactions and tasks.
Key elements of UI design include:
Layout and Structure: Organizing content and elements in a logical and visually appealing manner, ensuring easy navigation and readability.
Typography: Choosing appropriate fonts and text styles that are easy to read and convey the right tone.
Colors: Selecting a color scheme that reflects the brand identity, enhances readability, and guides user attention.
Icons and Images: Creating or selecting icons and images that communicate effectively and enhance the user experience.
Buttons and Interactive Elements: Designing buttons, links, and other interactive elements to be visually distinct and easy to click or tap.
Forms and Input Fields: Designing forms and input fields to be user-friendly and intuitive, minimizing errors and friction.
User Experience (UX):
UX, or User Experience, focuses on the overall experience that a user has while interacting with a digital product. It goes beyond just the visual design and encompasses all aspects of a user's interaction, emotions, and perceptions. The goal of UX design is to create a product that is enjoyable, efficient, and meaningful for users.
Key aspects of UX design include:
User Research: Understanding user behaviors, needs, goals, and pain points through methods like surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
Information Architecture: Organizing content and features in a way that is easy to understand and navigate.
Usability: Ensuring that the product is easy to use, intuitive, and efficient, minimizing user frustration and errors.
Accessibility: Designing the product to be usable by a diverse range of users, including those with disabilities, by following accessibility guidelines.
Interaction Design: Defining how users will interact with the product, including gestures, animations, and transitions.
Prototyping and Testing: Creating prototypes to test and validate design ideas, making improvements based on user feedback.
Emotional Design: Creating an emotional connection with users by evoking positive emotions and providing a satisfying experience.
In summary, UI and UX are closely related disciplines that work together to create a successful digital product. UI focuses on the visual design and interactive elements, while UX encompasses the overall user experience, including usability, accessibility, and emotional engagement. Both UI and UX play crucial roles in ensuring that users have a positive and meaningful interaction with a digital product.

- Managerial Effectiveness!
- Future and Predictions
- Motivatinal / Inspiring
- Outro
- Entrepreneurship
- Mentoring & Guidance
- Marketing
- Networking
- HR & Recruiting
- Literature
- Shopping
- Career Management & Advancement

 SkillClick
SkillClick