Inquire
The Crucial Role of Cryptography in Cybersecurity: Safeguarding Data and Trust in the Digital Age"
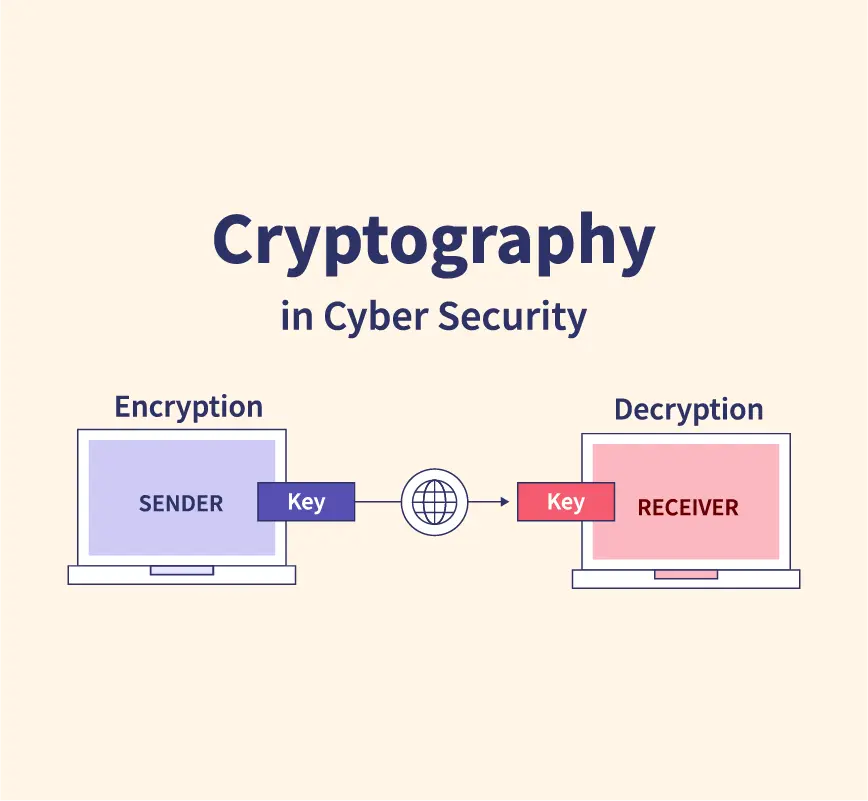
Cryptography is the science and practice of secure communication in the presence of adversaries. It involves the use of mathematical algorithms and techniques to encode information in a way that only authorized parties can understand or decipher, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation of data. Cryptography plays a crucial role in modern digital communication, protecting sensitive information, securing transactions, and safeguarding data from unauthorized access or tampering.
Cryptography is a fundamental tool used in cybersecurity to address various challenges and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data and communications.
Here are some key purposes of cryptography in cybersecurity:
1. Data Encryption:
Cryptography is used to encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access or interception during transmission or storage. Encrypted data can only be decrypted and accessed by authorized parties with the appropriate decryption key.
2. Secure Communication:
Cryptographic protocols, such as SSL/TLS, are used to establish secure connections between clients and servers, ensuring that data transmitted over the internet remains confidential and protected from eavesdropping or tampering.
3. User Authentication:
Cryptography is used in various authentication mechanisms, including password hashing, public-private key pairs, and digital certificates, to verify the identities of users and prevent unauthorized access to systems and resources.
4. Digital Signatures:
Cryptography enables the creation of digital signatures to authenticate the origin and integrity of digital documents, messages, or software updates. Digital signatures provide non-repudiation, ensuring that the sender cannot deny sending the information.
5. Secure Storage:
Cryptography is employed to protect data at rest by encrypting files, databases, and storage devices. This safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access, even if physical devices are compromised.
6. Secure Password Management:
Cryptography is used to securely store and manage passwords by hashing and salting them, making it difficult for attackers to reverse-engineer the original passwords from the stored values.
7. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):
PKI is a framework that uses cryptographic techniques to manage digital certificates and facilitate secure communication, authentication, and data integrity in various applications, such as secure email, digital signatures, and VPNs.
8. Secure Multi-Party Computation:
Cryptography enables secure computations across multiple parties without revealing sensitive data. This allows parties to perform joint computations while maintaining privacy and confidentiality.
9. Protection against Malware and Cyber Attacks:
Cryptography is used in various cybersecurity protocols and solutions to detect and prevent malware, ransomware, and other cyber threats. Techniques like digital signatures and hash functions help verify the authenticity of software and detect tampering.
10. Blockchain Security:
Cryptography is the backbone of blockchain technology, ensuring the security and immutability of transaction records in decentralized, distributed ledgers like those used in cryptocurrencies.
- In essence, cryptography is a critical component of cybersecurity, providing the essential tools and techniques to protect data, communications, and digital assets from malicious actors and ensuring the overall security and trustworthiness of digital systems and transactions.
Cryptography is used for various purposes across different domains to ensure secure communication, protect sensitive data, and enhance the overall security of digital systems.
Here are some common applications of cryptography:
1. Secure Communication:
Cryptography is used to encrypt messages and data transmitted over communication channels, such as the internet, to prevent unauthorized interception and eavesdropping. It ensures that only the intended recipient can decipher and read the message.
2. Data Protection:
Cryptography helps protect sensitive data, such as personal information, financial details, and intellectual property, by encrypting it when stored on servers or transmitted between systems. This guards against data breaches and unauthorized access.
3. Digital Signatures:
Cryptography enables the creation of digital signatures, which serve as a way to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital documents, messages, or transactions. Digital signatures provide non-repudiation, ensuring that the sender cannot deny sending the information.
4. Secure Transactions:
Cryptography is essential for securing online transactions, such as e-commerce purchases and online banking. It ensures that sensitive financial data, such as credit card numbers and passwords, is transmitted securely and remains confidential.
5. Authentication:
Cryptographic techniques are used for user authentication, ensuring that only authorized users can access specific systems, websites, or resources. This helps prevent unauthorized access and protects against identity theft.
6. Password Protection:
Cryptography is employed to securely store and manage passwords. Instead of storing actual passwords, systems typically store encrypted versions (hashes) to prevent exposure in case of a data breach.
7. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs):
VPNs use cryptography to create secure, encrypted tunnels over the internet, allowing users to access private networks and resources from remote locations while ensuring data confidentiality.
8. Blockchain Technology:
Cryptography forms the foundation of blockchain technology, ensuring the security and immutability of transaction records in decentralized, distributed ledgers like those used in cryptocurrencies.
9. Digital Rights Management (DRM):
Cryptography is utilized in DRM systems to protect copyrighted content from unauthorized distribution and ensure that content can only be accessed by licensed users.
10. Secure Software Updates:
Cryptographic techniques are employed to verify the authenticity and integrity of software updates, ensuring that users receive legitimate and untampered updates from trusted sources.
- In summary, cryptography plays a vital role in securing digital communication, protecting sensitive data, and building trust in the digital world.
- Its applications are vast and crucial for maintaining privacy, authenticity, and data integrity in today's interconnected and data-driven society.

- Managerial Effectiveness!
- Future and Predictions
- Motivatinal / Inspiring
- Other
- Entrepreneurship
- Mentoring & Guidance
- Marketing
- Networking
- HR & Recruiting
- Literature
- Shopping
- Career Management & Advancement

 SkillClick
SkillClick