Inquire
Insights into Quantum Computing Developments
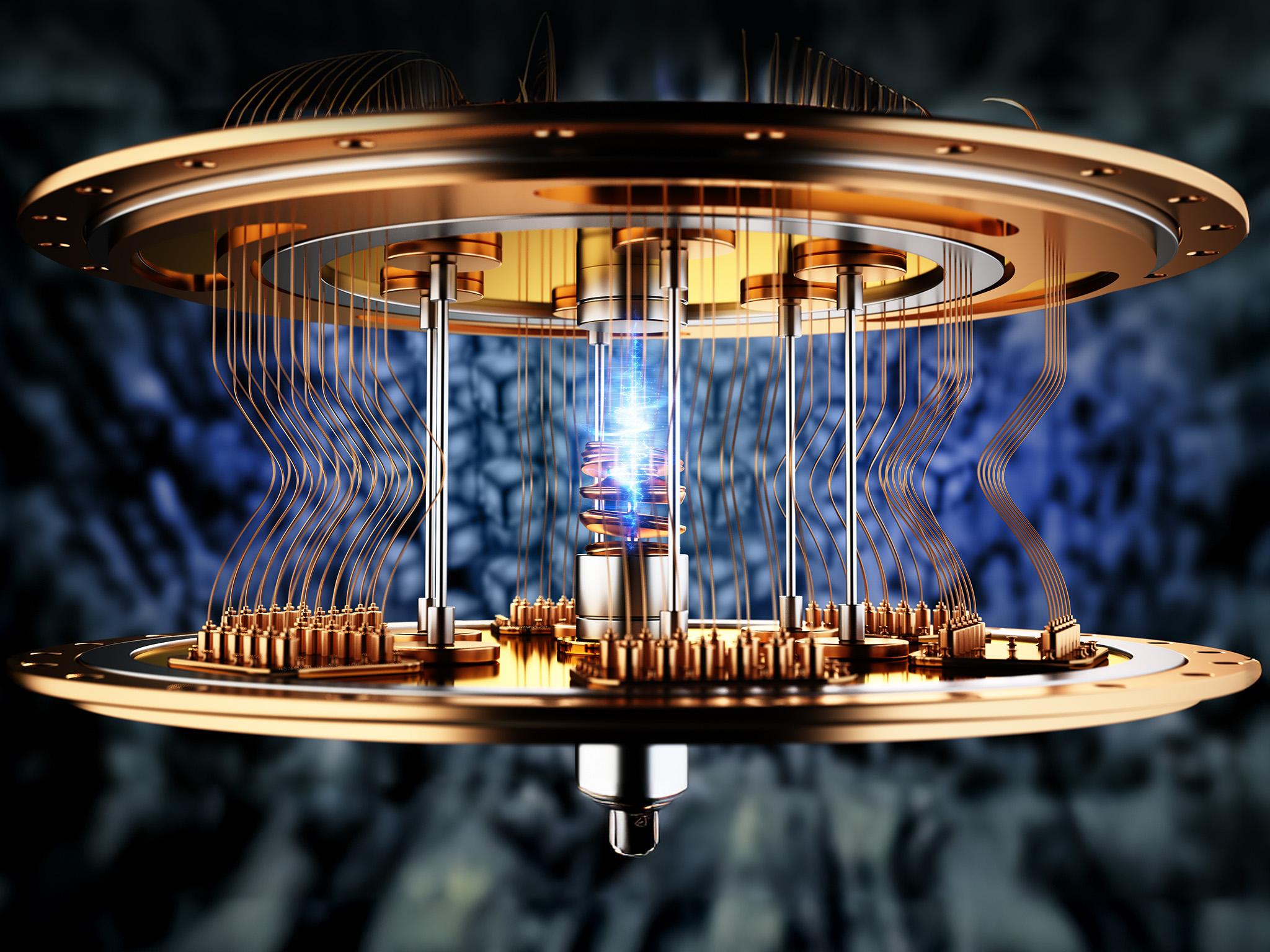
The structure of the emerging Indian Quantum Computing Report is uniquely defined by a deep and intentionally cultivated public-private partnership model. Unlike the purely private-sector-led ecosystem of the United States, or the more state-dominated model of China, India's approach is a hybrid one, where the government acts as the primary catalyst and strategic director, while actively encouraging and collaborating with the private sector. The National Quantum Mission (NQM) is the central framework for this partnership. The government is providing the substantial, long-term, high-risk funding for the fundamental research and the creation of the core national research infrastructure. This public investment is designed to de-risk the field and to create the foundational talent and technology base. The private sector—from large corporations to new startups—is then invited to partner with the government-funded research hubs to work on more applied, commercially-oriented projects. This collaborative model is designed to ensure that the public investment in research is closely aligned with the needs of the industry and that there is a clear pathway for translating scientific breakthroughs into commercial applications and economic value for the nation.
Key Players
The key players in this public-private ecosystem are clearly defined. On the public side, the key players are the Department of Science and Technology (DST), which manages the NQM, and the four Thematic Hubs located at premier academic institutions, which are the primary centers for research and collaboration. These hubs are explicitly designed to be public-private partnerships, with their governance structures often including representatives from both academia and industry. On the private side, the key players are a growing group of Indian and multinational corporations that have signed up as industry partners to these hubs. This includes major Indian technology companies like TCS, who are collaborating with the hubs on joint research projects and are also helping to shape the curriculum for new quantum education programs. It also includes major global companies with a significant presence in India who are keen to tap into the emerging talent pool. A third group of key players are the venture capital firms and corporate venture arms that are beginning to invest in the startups that are spinning out of this ecosystem.
Future in "Quantum Computing Report"
The future of this public-private partnership model in India will be about strengthening the linkages and creating a more seamless "lab-to-market" pipeline. The future will likely see the creation of more formal mechanisms for technology transfer from the national research hubs to the private sector, such as dedicated technology licensing offices and more streamlined policies for researchers who want to spin out their own companies. Another major future trend will be a greater financial co-investment from the private sector into the core research activities. As the technology matures and the commercial applications become clearer, large Indian corporations will be expected to move from being passive partners to being active co-investors in the national R&D effort. The future will also see the government using its procurement power as a tool to support the nascent domestic quantum industry. For example, a government agency might become the first customer for a new quantum security solution developed by an Indian startup. This collaborative model is seen as essential for competing with the massive scale of the private sector R&D in North America and the massive state-led R&D in other parts of APAC.
Key Points "Quantum Computing Report"
This analysis highlights several crucial points about India's public-private partnership model for quantum. The primary model is a government-led strategy that actively fosters collaboration with the private sector through the framework of the National Quantum Mission. The key players are the government-funded research hubs and their industry partners, including major Indian tech companies and a growing startup ecosystem. The future is about strengthening this partnership to create a more efficient "lab-to-market" pipeline and encouraging greater private sector co-investment. This hybrid, collaborative approach is a defining characteristic of India's national strategy and is seen as the most effective way to build a competitive and self-sustaining quantum industry. The Quantum Computing Report is projected to grow to USD 14.19 Billion by 2035, exhibiting a CAGR of 27.04% during the forecast period 2025-2035.
Top Trending Reports -
Web Application Firewall Market Size
- Managerial Effectiveness!
- Future and Predictions
- Motivatinal / Inspiring
- Other
- Entrepreneurship
- Mentoring & Guidance
- Marketing
- Networking
- HR & Recruiting
- Literature
- Shopping
- Career Management & Advancement

 SkillClick
SkillClick